From the moment we first meet with patients,
we will take care of them like a family with faith, hope, and love.
Wellness Hospital treats even the hearts of customers through experts treatment and specialized medical services.
In general, men have more developed muscle tissues than adipose tissues, and women have more adipose tissues than muscle tissues. It is considered normal to have a body fat mass of about 22%. Obesity is defined as a state in which the amount of body fat exceeds the range of 25% or more for men and 30% or more for women. Your body shape depends on this body-fat percentage, and understanding your body shape is the first step in controlling your weight loss efforts. It should not be forgotten that obesity is not only an aesthetic problem, but also a medical problem that may result in other severe diseases. Obesity is now classified as a disease because it may cause various adult diseases such as blood pressure problems, diabetes, heart diseases, and vascular diseases.
-
1
Genetic factors
It has been demonstrated in several studies that obesity is inherited. Factors such as fat distribution type (abdominal obesity type or subcutaneous fat obesity type), degree of physical activities, basal metabolic rate that makes energy necessary for life, energy performance after overeating, lipid breakdown rate, and eating habits. About 30-50% of cases are related to genetic factors.
-
2
Environmental factors
It is reported that the modern, westernized environment consumes more foods with enormous calories, and the lifestyle is mainly sedentary, increasing the obesity rate. Various environmental factors related to dietary habits and cultural and socioeconomic status play an important role in obesity. These factors play an important role in inducing obesity by influencing diet habits and degree and range of one’s physical activities.
-
3
Psychological factors
It's a well-known fact that you change your eating habits to deal with stress. The more stress you have, the easier it is to gain weight if you have no other measures to deal with it.
-
4
Imbalance of energy metabolism
If the balance of caloric intake and energy burnt out is broken, obesity may occur. In case of excessive caloric intake, insulin secretion increases, which promotes fat storage in the body.
-
5
Secondary (Symptomatic) Obesity
Secondary obesity refers to a case in which there is a disease or drug that has led to obesity. Obesity-causing diseases include hypothyroidism, Cushing's syndrome due to excessive adrenocortical hormone, and polycystic ovary syndrome. In these cases, obesity can be treated only when the underlying diseases are treated together.
-
· Body Fat Ratio Measurement
Although there are various methods for measuring body fat, a body fat measuring instrument with simplicity and high accuracy is widely used.
-
· Calculating Body Mass Index (BMI)
BMI is a value obtained by dividing the weight by the square of the height (measured in meters), and it is easy to calculate. In the case of Western people, it reflects body fat relatively accurately, and the measured value can be used to predict prognosis, such as one’s lifespan. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines someone as overweight if his/her BMI is over 25 and obese if it’s over 30, but for Koreans, whose physique is different from that of Westerners, it seems reasonable to classify over 23 as overweight and over 25 as obese. However, since it is a method of determining the degree of obesity only by height and weight, it has serious limitations, and it seems that there are many limitations in its application to Koreans, because it is developed based on statistics of Western people.
-
· Diagnosis of Abdominal Obesity
A simple method of diagnosing abdominal obesity is to use the waist-hip ratio, which is a value obtained by dividing the waist circumference by the hip circumference. If it is 0.9 for men and 0.85 for women, it can be diagnosed as abdominal obesity. However, recently, some say that the waist circumference reflects the amount of abdominal fat better than the waist-hip circumference and diagnose only with the waist circumference. do. Obesity in which fat is mainly accumulated in the upper body is called abdominal obesity or male-type obesity, and complications of obesity such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and hyperlipidemia are closely related to abdominal obesity. In particular, abdominal obesity is more dangerous than lower body obesity.
-
· Calculation Method Using Standard Weight
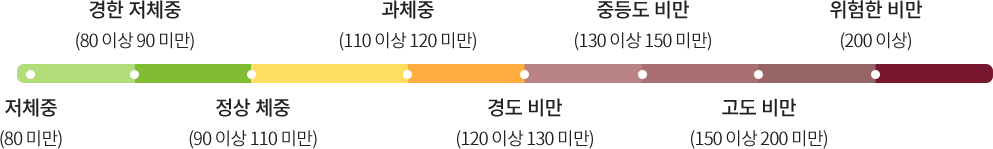
The degree of obesity is calculated by calculating how much the actual weight exceeds the standard weight. If the degree of obesity exceeds 120%, it is judged as obesity, but there are many limitations because it is diagnosed simply by weight.
Calculation method
· Standard weight(kg) = (Current height cm - 100) × 0.9
· Obesity(%) = (Current weight ÷ Standard weight) × 100
Obesity determination
· Mild underweight - 80 to less than 90
· Overweight - 110 to less than 120
· Moderate obesity - 130 or more but less than 150
· Dangerous obesity (requires immediate actions) - over 200
· Underweight - Less than 80
· Normal weight - 90 to less than 110
· Mild obesity - 120 but less than 130
· Severe obesity - 150 to less than 200
4
Treatment Methods and Procedures
-
1
Measurement of obesity, body composition analysis
Based on body composition analysis, set goals for body fat mass and muscle mass to reach the ideal body condition, not just for weight control.
-
2
Medical consultation
Through the guidance of the medical specialist, examine your current and past medical history and analyze the health risk and decide whether to receive treatment.
-
3
Comprehensive obesity test
Based on individual medical conditions and lifestyle, you will receive systematic treatment for safe weight loss as well as maintenance of the lost weight.
Comprehensive obesity test
-
· Electrocardiography, chest X-ray, and lung function measurement
-
· Thyroid and abdominal ultrasound (examination of liver, kidneys, gallbladder, pancreas, uterus, ovaries, bladder, etc
-
· Sleep gastroscopy
-
· Blood and urine tests : anemia test, hyperlipidemia test, liver function test, kidney function test, electrolyte test, thyroid test, hepatitis test
-
· Hormone test : thyroid hormone, thyroid hormone, corticosteroid, female hormone test
-
· Bone density test
Indiscriminate binge eating or overeating causes digestive problems and obesity, and conversely, eating like a bird can damage health even more due to malnutrition and lack of metabolism. Complete fasting can be attempted for a short period of time in severe obesity, but it is better to avoid it as it can result in side effects, such as electrolyte imbalance and severe protein loss.